We like to share product recommendations with you and hope you like them! Just to make you aware Water Filter Data may collect a small share of sales or other compensation from the links on this page.
If you’re looking for filtered water, you’ve most likely come across the advice to use a reverse osmosis water purification device. If you are concerned about contaminants, you might have learned that drinking purified water is a good idea. If you’ve ever wondered what the difference is between distilled and filtered water, the response is that distillation is simply a form of water purification. So, rather than thinking of this as purified vs distilled water, it is a better representation to think of distilled water as part of purified water. Reverse osmosis vs distilled water, both are popular methods for water purification, but what are the differences between these two methods, and which is better?
Although water distillation is an older purification method, it is less suitable for home water purification due to a number of factors. Reverse osmosis vs distilled water, understanding the distinctions will help you decide which form of water purification is better for you.
What exactly is Distilled Water?
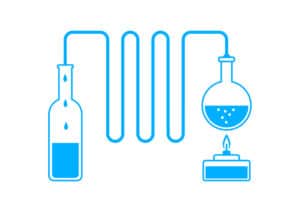
Distilled water is water that has gone through the distillation process. To distill water, boil it, collect the steam that rises from it, and then allow the steam to condense and fill another jar.
In other words, the distillation process involves converting liquid water into a gas and then back into a liquid. Distillation necessitates the use of a still, which is a piece of equipment. By automating the procedure, modern distillation units are relatively simple to operate.
Distillation is the process of purifying water. Distillation is a method of eliminating pollutants and providing clean water, as purification is the process of extracting specific contaminants from water. Distillation, like other methods of water filtration or purification, cannot eliminate all pollutants on its own.
Distillation is an efficient process for extracting dissolved solids in water, such as minerals and salts. These compounds harden the water and cause scaling. Distillation is also effective at removing bacteria from water, such as giardia or Legionella.
Distillation is less effective at extracting contaminants that have a boiling point close to that of water. To extract these contaminants, purified water must be subjected to additional filtration.
Certain types of equipment need distilled water to work. It will be needed for use in equipment that may be harmed by mineral deposits. In the house, distilled water is used in an electric iron or steam mop, as well as in automobile cooling systems and some types of batteries.
What are the Drawbacks of Distillation?
While distillation has some purification benefits, there are some disadvantages to consider. When comparing reverse osmosis water filter vs distilled water, the most important drawbacks of distillation are speed and energy costs.
As compared to alternatives such as reverse osmosis, home distillation systems require a significant amount of energy to operate, resulting in higher ongoing costs.
Distillation systems have a drawback when it comes to supplying on-demand drinking water. Although the best under sink reverse osmosis device can produce up to 75 gallons of drinking water per day, distillation takes time. Water must be brought to a boil, and the resulting steam must condense and settle in a bottle.
The second downside to distilled water is that the majority of people dislike drinking it. Distilled water has been demineralized and is commonly characterized as having a flat or bland taste. If you’re curious what demineralized water is, it’s actually water that has had the dissolved minerals and salts extracted.
Minerals and salts such as magnesium and calcium, which harden water, also contribute to the flavor that many of us have come to expect. Many people find the taste odd since distillation almost completely eliminates all mineral content in water.
What exactly is Reverse Osmosis Filtering?

Reverse osmosis is a common water filtration device in both residential and commercial settings. Millions of people depend on reverse osmosis to provide safe, filtered drinking water. It is also used in desalination plants to convert seawater to freshwater, in industrial agriculture to regulate the pH of the soil, in the production of pharmaceutical products, and in the production of food and beverages.
The easiest way to explain reverse osmosis is to first understand how osmosis functions. Osmosis is a natural process that involves the movement of a solvent through a semipermeable membrane from a solution with a low concentration of solutes to a solution with a high concentration of solutes.
The cause of this movement is a force known as osmotic strain.
- Solutes are particles that are dissolved in a solution.
- A solvent is a liquid that is present in a solution.
- Solute and solvent mixture to form a solution.
- Semi-permeable membrane – This is a membrane that allows certain substances but not others to move through.
Osmosis seeks to maintain equilibrium on both sides of a membrane. If one side of the membrane has a higher concentration of solutes and a lower concentration of liquid, liquid flows from the other side until the solution on both sides is the same. Osmosis is the process by which plants obtain nutrients from the soil. The soil is a solution of a low solute concentration, while the plant has a high solute concentration.
The water reaches the plant through the semipermeable membrane of the roots. This whole process is reversed in reverse osmosis. The method of reverse osmosis begins with a solution containing a high concentration of solutes. This is water with a high concentration of pollutants for water purification.
This polluted water is propelled through a semipermeable membrane at high pressure. The semipermeable membrane contains tiny pores that allow water molecules to move through while keeping other pollutants at bay. The desalination process is an ideal way to see the reverse osmosis process in motion. Desalination plants push salty seawater through a semipermeable membrane, which allows water molecules to move but holds salt out. What remains on the other hand is safe, potable water.
If you’re asking, “Is reverse osmosis water safe?” the response is that it contains far fewer pollutants than unfiltered tap water.
As a filtration device, reverse osmosis is efficient at reducing or eliminating a variety of pollutants. There are some examples:
- Minerals.
- Salts.
- Microbes.
In a residential environment, reverse osmosis systems can also include pre-and post-filters. Before the water passes through the membrane, the pre-filter eliminates any sediment. This contributes to the membrane’s longevity. The post-filter employs granulated activated carbon (GAC), which captures certain pollutants that reverse osmosis systems do not. Disinfectants such as chlorine, disinfection byproducts, volatile organic chemicals (VOCs), synthetic organic chemicals (SOCs), and other substances that change the taste or smell of water are examples of these.
There are a few key points to note about residential reverse osmosis water filtration systems. The first is that they are not absolutely effective. A small volume of water, along with any pollutants accumulated during the process, is flushed down the drain. The second thing to keep in mind is that the system’s filters and RO membrane will need to be replaced on occasion. This is normally an easy process with little system downtime, but it is essential to keep the system running at peak efficiency.
When choosing between a reverse osmosis water filter and a purified water filter, bear in mind that both types of systems generate some form of wastewater. Contaminants accumulate on one side of the process in all types of systems and must be flushed from the system.
Reverse Osmosis Vs Distilled Water: Difference
Residential water distillers are available, but they consume a lot of energy and are much less popular than reverse osmosis filters. Having clean water is as easy as turning on your faucet with a reverse osmosis filter. The process runs without your intervention, while the distillation process is much more active. Again, it is not as easy as boiling water and calling it a day as many people believe. Distillation also usually produces much less water than most people need.
More on Minerals
We already discussed that reverse osmosis and distillation both extract minerals from water. This leads to a common misunderstanding. Mineral amounts in water are not harmful to your health, but they can damage your plumbing and appliances. The minerals in standard tap water will build up within the iron, creating clogs and other problems, which is why steam iron manufacturers usually prefer using distilled water. This occurs in pipes, showerheads, and dishwashers as well.
Although the difference in mineral removal between reverse osmosis and distilled water is minor, neither method is appropriate for any application that requires mineral-free water. You wouldn’t add a reverse osmosis device to your showerhead, for example. Similarly, you can not use a water distiller to make shower water. Any of these methods will be wasteful. Instead, you’d like a water softener. The ability to generate enough soft water for your entire house is one of the most impressive features of these systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it alright to drink distilled water??
Technically, you should drink purified water. Nothing negative is going to happen to you. However, the flavor can appear flat. A lack of minerals would not harm you either, since the majority of our mineral intake comes from food rather than water.
What is the method for producing distilled water??
Producing distilled water necessitates the use of specialized equipment. This apparatus will boil the water, collect the condensation, and allow it to cool back into water.
Is distilled water the same as boiling water?
No, boiling water kills organic impurities in water, but without the condensation capture mechanism, its utility is minimal.
What is the purpose of distilled water?
Most people use purified water in appliances, machinery, and tests that require extremely pure, mineral-free water.
Reverse Osmosis Vs Distilled Water: Wrap Up
Both distillation and reverse osmosis are water purification processes, but they work in different ways. The distillation method entails boiling water, collecting the resulting steam, and condensing the steam in a separate tube. This operation is carried out using a specialized piece of equipment known as a still.
Although distillation is efficient at extracting bacteria, minerals, and salts from water, it results in water that tastes flat and bland. Except in emergencies, distillation is simply too sluggish, cumbersome, and inaccessible as a form of home water purification.
In comparison, reverse osmosis filtration systems use high pressure to push contaminated water through a specialized semi-permeable membrane. The membrane in a reverse osmosis system is built to allow water molecules to move through but not other contaminants.
Reverse osmosis devices, when combined with an activated carbon post-filter, are capable of extracting minerals, salts, and bacteria from water, as well as many organic and synthetic chemicals, disinfectants, and their byproducts.

Wayne is a water quality expert – The founder of Water Filter Data. He has a degree in microbiology and his field of expertise is drinking water. His goal is to allow for clean and healthy water for as many people as possible.



